xCAT Node Installation HOWTO (WIP)
Installation Methods
xCAT Installation Process
How to Install a Node
The purpose of this document is to describe the various methods to remotely install an OS with xCAT.
This document assumes that xCAT 1.2.0 or later is installed and that your management server is configured. Read the xCAT-mini-HOWTO for details.
The term noderange refers to xCAT's internal facility to perform an operation on a range of nodes, please read the noderange.5 man page for details.
Look to the $XCATROOT/sameples/etc files for a place to start.
xCAT supports the following automated unattended network installation methods:
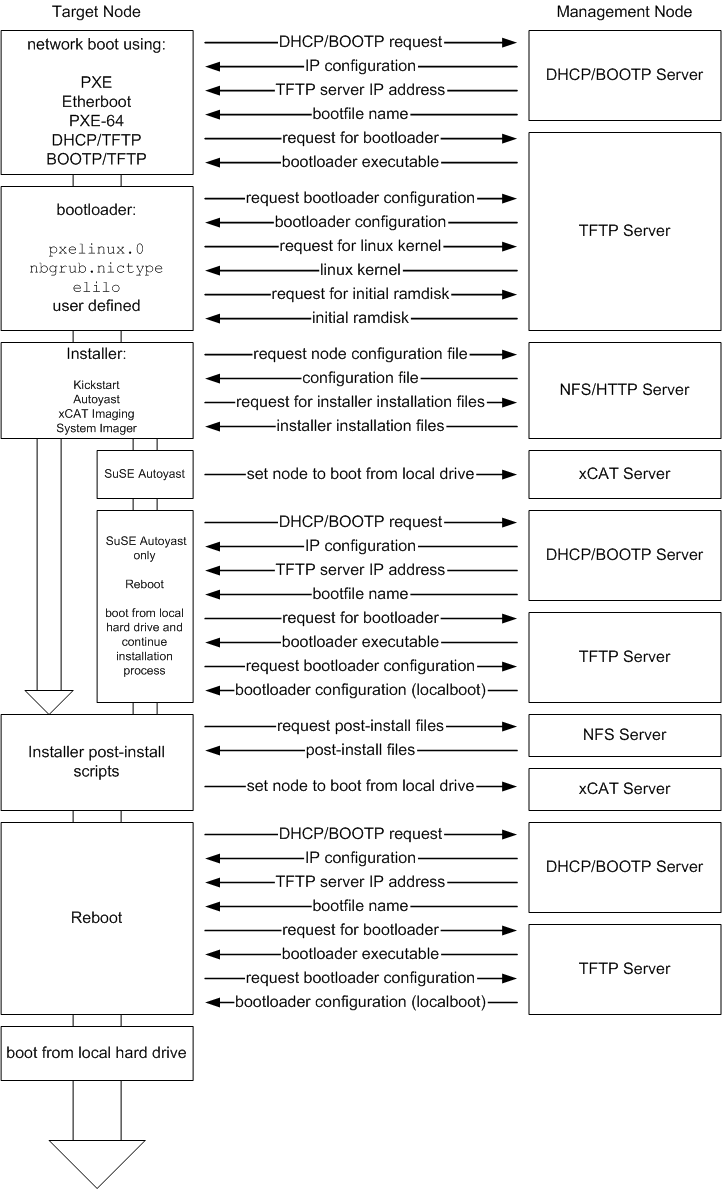
The xCAT node installation process is best illustrated by the following diagram:

| PXE | The x86 and x86_64 industry standard for
network booting. Most network adapters and on-board NICs support PXE.
It is necessary that all nodes supporting PXE boot the network before
local hard drive or xCAT will fail to force the node to install.
Please read the xCAT Stage1 HOWTO for more
details. |
| Etherboot/GRUB | Etherboot provides a method for
non-PXE enabled machines to net boot. xCAT Etherboot support uses
standard Etherboot floppies or CDs but chains to
nbgrub as the bootloader.
It is necessary that all nodes using Etherboot boot the floppy/CD-ROM
before local hard drive or xCAT will fail to force the node to install.
Use the xCAT command makebootdisk
to create boot floppies and CDs. |
| PXE64 | The ia64 Intel standard for
network booting. All EFI-based ia64 machines support PXE64 on the
on-board NIC. It is necessary that all nodes using EFI/PXE64 have an
EFI entry "Ethernet" as the first entry. Please read the
xCAT Stage1 HOWTO for more details. |
| CHRP | The ppc64 standard for booting. PPC64-based machines boot OpenFirmware and require a serial console monitor to switch from network to HD boot. For each node/blade sol.bc must be setup in $XCATROOT/etc/conserver.cf and rbootseq run to boot HD before Network. Currently only Bladecenter JS20 is supported. |
| User Defined | If you have a boot loader for terminal servers, switches, or nodes that is not included with xCAT simply place in /tftpboot (or whatever you defined in $XCATROOT/etc/site.tab as tftpdir). |
The network bootloader is defined for each node in $XCATROOT/etc/nodehm.tab. Valid values are:
| pxe | For PXE enabled nodes. |
| nbgrub | For Etherboot/GRUB enabled
nodes. |
| elilo | For PXE64 enabled nodes. |
| chrp | For ppc64 nodes (JS20). |
| file:filename | For user defined where filename is the file to be TFTP downloaded and executed from /tftpboot (or whatever you defined in $XCATROOT/etc/site.tab as tftpdir). |
| PXE |
/tftpboot/pxelinux.0 |
| Etherboot/GRUB |
/tftpboot/grub/nbgrub.nic
where nic is defined in
$XCATROOT/etc/nodehm.tab as
eth0 |
| PXE64 |
/tftpboot/elilo.efi |
| CHRP |
/tftpboot/chrp/nodename.img
(A symlink set to point to the correct combined compressed kernel/initrd
image in /tftpboot/xcat/OSVER/ARCH) |
| User Defined | /tftpboot/filename (as defined in $XCATROOT/etc/nodehm.tab as file:filename) |
Bootloader configuration file location:
| PXE |
/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/filename.
Where filename is the hex equivalent of the IP address of the
node (e.g. 199.88.179.201
would be C758B3C9). If
the node specific configuration file is missing then the file
default is used to boot the
local HD. |
| Etherboot/GRUB |
/tftpboot/grub/filename.
Where filename is nodename.grub. |
| PXE64 |
/tftpboot/elilo/filename.
Where filename is the hex equivalent of the IP address of the
node with a .conf extension
(e.g. 199.88.179.201
would be C758B3C9.conf).
A link IP address .conf file is
also created for backwards compatibility with older xCAT
elilo.efi bootloaders. |
| CHRP | /tftpboot/chrp/filename. Where filename is nodename. |
The bootloader configuratoins files, kernels, and initrd images, are placed in the appropriate TFTP directory automatically when rinstall, winstall, or nodeset is run.
NOTE: Previous versions of xCAT required that a script (mkks,
mkimage,
mk*, etc...) was run to create the
files. This version of xCAT detects changes in template files and xCAT
.tab files and creates the necessary
files on demand.
After the installer starts it NFS downloads the installation configuration
file.
INSTALLDIR is the
installdir field in
$XCATROOT/site.tab,
OSVER is the OS to be installed, and
ARCH is the hardware architecture
type. Installation configuration are located in:
INSTALLDIR/scripts/OSVER/ARCH
The name of the installation configuration is based on the resource group and
node type defined in $XCATROOT/etc/noderes.tab
and $XCATROOT/etc/nodetype.tab.
After the installation configuration file is parsed installation begins
installing from the installation sources:
INSTALLDIR/OSVER/ARCH
The command rinstall calls nodeset to setup the bootloader configuration file and the node installation configuration file then forces the node to boot (rpower noderange boot) and initiates the installation.
Determining what to install on each node
How does xCAT know what to put on each node? That is entirely up to
you. All the files in $XCATROOT/etc
play a part in the characteristics of the node namely
noderes.tab,
nodehm.tab,
nodetype.tab.
noderes.tab contains most of the
information on where to install from and other common characteristics of each
node. nodehm.tab also plays a
role in how to install and other hardware related setup.
nodetype.tab directly relates to the
installation type and template that will be used for each node.
Use the command nodels to display what
will be installed on each node.
E.g.
nodels node[1-4] install
Output:
node1: suse81-x86-compute-s0
node2: sles8-x86_64-dev-opteron
node3: rhas21-ia64-compute-tiger
node4: sles8-ia64-compute-tiger2
In other words:
nodename: OS Version-Architecture-Template name (nodetype.tab)-Resource group (noderes.tab).
Kickstart and Autoyast Templates
Define a template (.tmpl file) in $XCATROOT/install/OSVER/ARCH. The name of the template file will be the image type in $XCATROOT/etc/nodetype.tab. Sample files are located in $XCATROOT/install/OSVER/ARCH/base. When xCAT is looking for .tmpl files it will look in $XCATROOT/install/OSVER/ARCH before $XCATROOT/install/OSVER/ARCH/base. So feel free to use the base files as-is. WARNING: Do NOT modify the base files. xCAT updates will replace them. Files in $XCATROOT/install/OSVER/ARCH will be safe.
.tmpl files ARE standard Kickstart and Autoyast files. Please read Kickstart and Autoyast documentation for details. There are a few exceptions.
Variable Substitution
Variables are defined as #VAR# where VAR may be (listed by precedence):
| MASTER | Management Server Hostname |
| MASTER_IP | Management Server IP |
| MASTER_IPS | All Mangement Server IPs (for multi homed, routed clusters) |
| RSH | Using RSH Y or N |
| OSVER | OS Version as defined in $XCATROOT/etc/nodetype.tab |
| ARCH | Architecture as defined in $XCATROOT/etc/nodetype.tab |
| NODERES | Node resource group |
| NODETYPE | Node image/template type as defined in $XCATROOT/etc/nodetype.tab |
| INSTALL_NFS | NFS installation server as defined in $XCATROOT/etc/noderes.tab |
| INSTALL_NFS_IP | NFS installation server IP as defined in DNS |
| INSTALL_SRC_DIR | Installation source directory. installdir as defined in $XCATROOT/etc/site.tab/OSVER/ARCH, e.g. /install/rh73/x86 |
| INSTALL_CF_DIR | Installation configuration directory. installdir as defined in $XCATROOT/etc/site.tab/scripts/OSVER/ARCH, e.g. /install/scripts/rh73/x86 |
| INSTALL_CF_FILE | Installation configuration file name in INSTALL_CF_DIR |
| KERNEL | Kernel name |
| INITRD | Initrd name |
$XCATROOT/lib/functions variables for field numbers for TABLE lookups:
| nodehm_power | |
| nodehm_reset | |
| nodehm_cad | |
| nodehm_vitals | |
| nodehm_inv | |
| nodehm_cons | |
| nodehm_bioscons | |
| nodehm_eventlogs | |
| nodehm_getmacs | |
| nodehm_netboot | |
| nodehm_eth0 | |
| nodehm_gcons | |
| nodehm_serialbios | |
| nodehm_beacon | |
| nodehm_bootseq | |
| nodehm_serialbps | |
| noderes_tftp | |
| noderes_nfs_install | |
| noderes_install_dir | |
| noderes_serial | |
| noderes_usenis | |
| noderes_install_roll | |
| noderes_acct | |
| noderes_gm | |
| noderes_pbs | |
| noderes_access | |
| noderes_gpfs | |
| noderes_netdevice | |
| noderes_prinic | |
| nodetype_osver | |
| nodetype_arch | |
| nodetype_image |
Support
Egan Ford
egan@us.ibm.com
August 2004